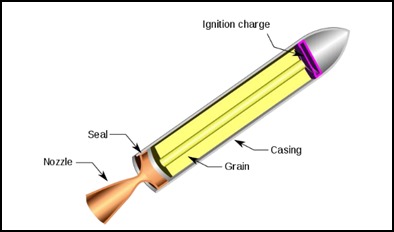
La tecnología de motores de propulsante sólido se utiliza comúnmente debido a su confiabilidad, rentabilidad y diseño simple. Sin embargo, conlleva un riesgo de fallas que pueden dañar a seres humanos, o el medio ambiente y causar pérdidas a los activos. En este artículo, se estudia una evaluación de riesgos para motores de cohetes de propulsante sólido (SRM). Los SRM son básicamente dispositivos que transforman la energía química del propulsante sólido en empuje (energía cinética) en un recipiente que funciona como un recipiente a presión. El HAZOP es excelente para identificar modos de falla sistemáticamente mediante la identificación de la desviación de los parámetros físicos del proceso, pero tiene dificultades para priorizar el riesgo. El FMEA es eficaz para comprender los mecanismos de falla y establecer las contramedidas necesarias, pero para un producto con muchos componentes, la hoja de trabajo también es compleja. Al combinar estos dos métodos, integrando la superioridad de cada método, esta investigación puede identificar modos, causas y efectos de fallas que pueden ocurrir en SRM de manera efectiva y precisa. Además, esta investigación también propone acciones correctivas o preventivas para cada modo de falla. Como objetivo de la evaluación de riesgos, los resultados de la investigación pueden utilizarse como insumo para que los diseñadores mejoren su diseño y como objetos de inspección y vigilancia para los funcionarios de control de calidad.
Abstract
The development of rockets in Indonesia has long been carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Agency (LAPAN), which has now been integrated into the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN). The Research Centre for Rocket Technology, which is one of the centres within BRIN, has been developing solid propellant-based rockets with a various sizes and types. Solid-propellant rocket technology is commonly used because of their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and simple design. However, this technology is one of the high-risk technologies, whose failure can harm humans, damage the environment and cause huge losses to assets. As a high-risk technology, risk assessment activities must be carried out, starting from the design, manufacturing, testing and up to the launching stage. In this paper, we studied a risk assessment for general Solid-propellant Rocket Motor (SRM). SRM is basically a device that processes chemical energyin solid propellant into thrust (kinetic energy) in a container that functions as a pressure vessel. The risk assessment methods commonly used in this technology are the HAZOP or FMEA methods. The HAZOP is excellent in identifying failure modes systematically through identifying the deviation of physical process parameters but has difficulties in prioritizing the risk. The FMEA has effectiveness in understanding failure mechanisms and establishing necessary countermeasures, but for a product with a lot of components, the worksheet is also complex. By combining these two methods, integrating the superiority of each method, this research can identify modes, causes and effects of failure that may occur in SRM effective and accurately. In addition, this research also proposes corrective or preventive actions for each failure mode. As the objective of the risk assessment, results of the research can be used as input for the designers to improve their design and as inspection and surveillance objects for QC officers.
![]() Fuente: https://semarakilmu.com.my
Fuente: https://semarakilmu.com.my