La Tecnología de Fabricación Aditiva (AM) permite producir estructuras complejas, que incluyan diferentes materiales y componentes personalizados, al tiempo que se logra un bajo costo, alta precisión y una producción rápida de piezas. El estado de madurez alcanzado actualmente por la tecnología de AM ha generado mucho interés en el ámbito de fabricación de cabezas de guerra de proyectiles. En este artículo se presentan las tendencias de desarrollo de las tecnologías de AM y sus diferentes alternativas.
Abstract
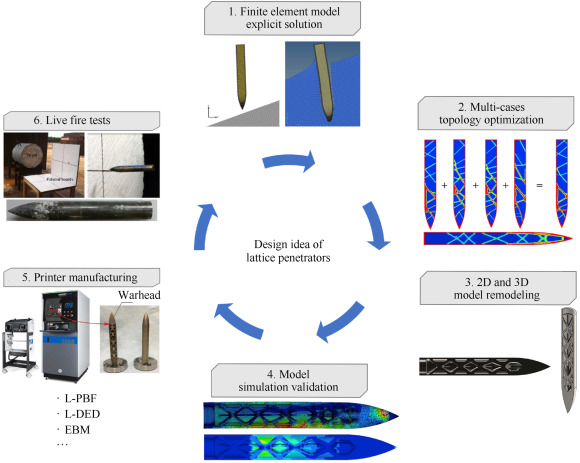
According to different damage modes, warheads are roughly divided into three types: fragmentation warheads, shaped charge warheads, and penetrating warheads. Due to limitations in material and structural manufacturing, traditional manufacturing methods make it difficult to fully utilize the damage ability of the warhead. Additive manufacturing (AM) technology can fabricate complex structures, with classified materials composition and customized components, while achieving low cost, high accuracy, and rapid production of the parts. The maturity of AM technology has brought about a new round of revolution in the field of warheads. In this paper, we first review the principles, classifications, and characteristics of different AM technologies. The development trends of AM technologies are pointed out, including multi-material AM technology, hybrid AM technology, and smart AM technology. From our survey, PBF, DED, and EBM technologies are mainly used to manufacture warhead damage elements. FDM and DIW technologies are mainly used to manufacture warhead charges. Then, the research on the application of AM technology in three types of warhead and warhead charges was reviewed and the existing problems and progress of AM technologies in each warhead were analyzed. Finally, we summarized the typical applications and look forward to the application prospects of AM technology in the field of warheads.
![]() Fuente: https://www.sciencedirect.com
Fuente: https://www.sciencedirect.com