Este estudio tiene como objetivo mejorar la estabilidad térmica de los fluidos espesantes por cizallamiento (STF) mediante la introducción de interacciones electrostáticas utilizando sílice modificada con carboxilo (C-SiO2), ácido poliacrílico (PAA) y cloruro de calcio (CaCl2). Los investigadores examinaron el comportamiento reológico del STF basado en C-SiO2 (CS-STF) en un rango de temperatura de 25 a 55 °C. A diferencia del STF basado en SiO2, que se espesa en un solo paso y disminuye la viscosidad con el aumento de la temperatura, el CS-STF exhibió un comportamiento de doble espesamiento, con una viscosidad máxima que alcanzó 1330 Pa·s a 35 °C. El estudio encontró que aumentar el contenido de CS-STF mejoró significativamente la resistencia al impacto de las telas de polietileno de peso molecular ultra alto (UHMWPE). En pruebas de impacto contundente, las telas con alto contenido de CS-STF experimentaron fallas de penetración a alta energía de impacto (18 J) debido a la concentración de tensión. Las pruebas de punción con cuchillos mostraron que los tejidos con un contenido adecuado de CS-STF tenían la mejor resistencia a la punción. Los hallazgos sugieren que el CS-STF de alto rendimiento, con su comportamiento de doble espesamiento y espesamiento por cizallamiento mejorado, tiene aplicaciones prometedoras en la protección personal contra impactos contundentes y punzantes.
Abstract
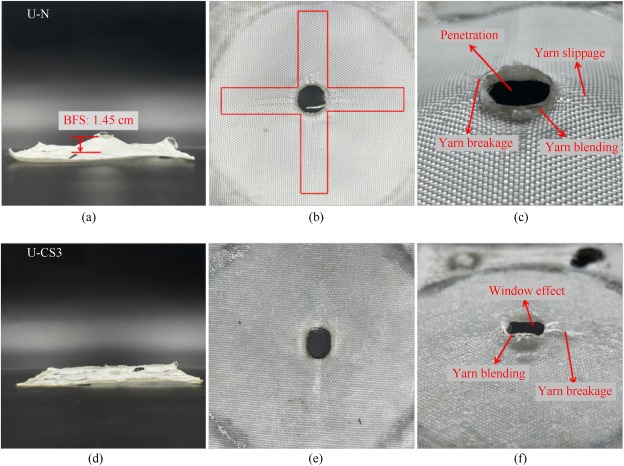
Inspired by the thermal stability mechanism of thermophilic protein, which presents ionic bonds that have better stability at higher temperatures, this paper proposes the introduction of electrostatic interactions by adding carboxyl-modified silica (C-SiO2), PAA, and CaCl2 to achieve higher viscosity over 25 °C. The rheological behavior of C-SiO2-based shear thickening fluid (CS-STF) was investigated at a temperature range of 25–55 °C. Unlike SiO2-based STF, which exhibits single-step thickening and a negative correlation between viscosity and temperature. As the C-SiO2 content was 41% (w/w) and the mass ratio of PAA:CaCl2:C-SiO2 was 3:1:10, the CS-STF displayed a double-thickening behavior, and the peak viscosity reached 1330 Pa·s at 35 °C. From the yarn pull-out test, the inter-yarn force was significantly increased with the increasing CS-STF content. Treating UHMWPE fabrics with CS-STF improved the impact resistance effectively. In the blunt impact test, the U-CS fabrics with high CS-STF content (121.45 wt%) experienced penetration failure under high impact energy (18 J) due to stress concentration caused by the shear thickening behavior. The knife stabbing test demonstrated that U-CS fabrics with appropriate content (88.38 wt%) have the best stabbing resistance in various impact energies. Overall, this study proposed a high-performence STF showing double-thickening and enhancing shear-thickening behavior at a wide temperature range, the composite fabrics with the performance of resisting both the blunt and stab impact had broad application prospects in the field of personal protection.
![]() Fuente: https://www.sciencedirect.com
Fuente: https://www.sciencedirect.com